SCS
0.5660


While humanity's efforts to curb planet-warming emissions are nowhere near enough to avoid heating the world to catastrophic levels, tentative improvements show that progress is possible.
The climate trajectory, while still poor, has improved since countries signed the Paris Agreement in 2015 and committed to limiting the global temperature rise to "well below" two degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, preferably a safer 1.5C.
And the uptake of renewable energy is providing a rare glimmer of hope.
- Heating -
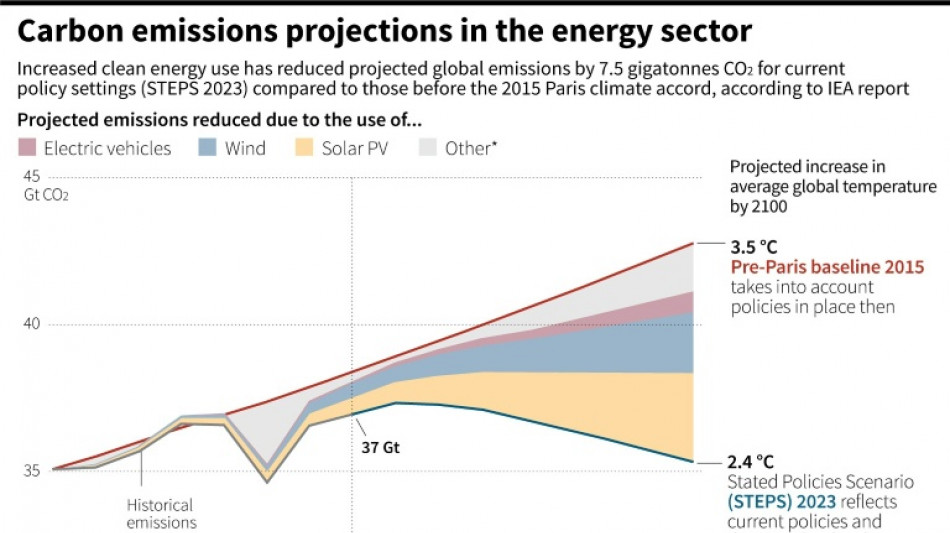
When the Paris Agreement was adopted, the global reliance on fossil fuels -- oil, gas and coal -- placed the world on a path towards a 3.5C rise in temperature by 2100 compared to the pre-industrial era, the International Energy Agency (IEA) said at the time.
Warming of that scale would prompt catastrophic climate disasters worldwide, including the risk of mass extinctions, the melting of glaciers and permafrost that could eventually unleash metres of sea level rise and unliveable conditions across much of the planet.
Eight years on, country commitments to reduce their carbon footprints have pulled that down slightly, putting the world on a path for a still-disastrous 2.5C to 2.9C by the end of the century, according to the UN's Environment Programme this month.
Every tenth of a degree of warming compounds the negative impacts on the climate, but the modest temperature reduction "reflects progress made in the transition to a lower emissions energy system since 2015", said the IEA.
But it "still falls far short of what is needed", the agency added.
- Peak emissions -
Annual greenhouse gas emissions responsible for climate change have risen roughly nine percent since COP21, according to UN data.
That increase led to record-breaking concentrations of CO2, methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O) in the atmosphere in 2022, the World Meteorological Organization said last week.
But the rate of the increase has slowed significantly.
The climate experts of the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) have projected that to meet the Paris goals, emissions need to peak by 2025.
To limit temperature rise to 1.5C emissions need to be slashed almost in half by 2030.
Recent estimates by the Climate Analytics institute find global emissions could peak by 2024 or even as early as this year.
The IEA in its pre-Paris deal assessment predicted that carbon dioxide emissions tied to the energy sector -- responsible for more than 80 percent of CO2 emitted by human activity -- could reach 43 gigatonnes (Gt) in 2030.
But the agency now says that current efforts mean that figure will be 35Gt by 2030.
That difference was "equal to the current combined energy sector emissions of the United States and European Union", it said.
- Rising renewables -
Three technologies -- solar, wind and electric vehicles -- are largely behind the improved global warming estimates since 2015.
"Solar PV is projected to reduce emissions by around three Gt in 2030," the OCED now estimates, "roughly equivalent to the emissions from all the world's cars on the road today."
Wind power is expected to reduce emissions by two gigatonnes in 2030 and electric vehicles (EVs) by around one gigatonne, compared to pre-Paris Agreement scenarios.
Photovoltaics (PVs) and wind power are expected to represent around 15 percent of global electricity production in 2030 - seven times the wind power and three times the PVs that the IEA predicted in 2015.
At the time, fleets of electric vehicles seemed a pipedream. The IEA anticipated that EVs would account for less than two percent of car sales by 2030.
It now estimates that more than a third will be purchases of electric vehicles by the end of the decade.
And the numbers are accelerating. "Clean energy technology adoption surged at an unprecedented pace over the last two years," said the IEA, noting a 50-percent increase in solar PV capacity and a 240-percent rise in EV sales.
The IEA attributes the progress -- unthinkable before the Paris Agreement -- to declining costs and public policy initiatives from China, the United States and Europe among others.
Five-year plans in China have raised ambitions for solar power and driven down global costs.
Off-shore wind projects in Europe "kick-started a global industry" and electric two-wheelers and buses "have seen significant uptake in India and other emerging markets", said the agency.
D.Ford--TFWP