RBGPF
59.6900


British monkeypox patients are exhibiting symptoms that differ from previous outbreaks, the first study examining UK cases said on Friday, leading researchers to call for the definition of the disease to be updated.
Until a few months ago, monkeypox had been largely confined to West and Central Africa, where new outbreaks were mostly caused by humans being infected with the virus by animals like rodents.
But since May, more than 3,400 cases have been recorded worldwide, the large majority of them in Western Europe among men who have sex with men and have no known links to the sub-Saharan African cases.
Britain detected some of the earliest new global cases and the first study into patients there was published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases journal on Friday.
The researchers analysed 54 monkeypox patients in London, all men who have sex with men, who represented 60 percent of UK cases as of May 26.
All but two were unaware they had been in contact with someone who had monkeypox.
A quarter of the men were HIV-positive and a quarter had a sexually transmitted disease while they had monkeypox.
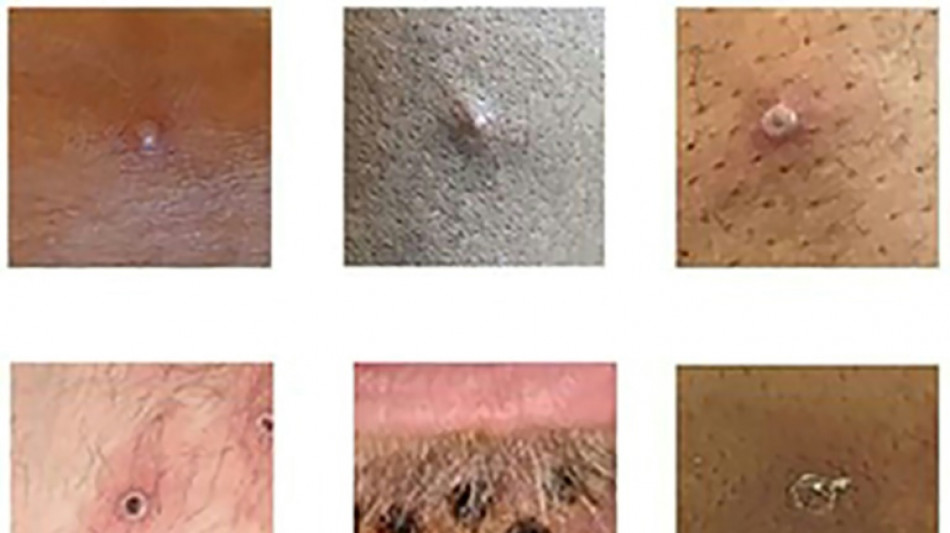
All patients had skin lesions, of which 94 percent were in the genital and anal areas.
These factors suggest that the virus is being transmitted during skin-to-skin contact as during sex, the study said.
The World Health Organization is investigating cases of semen testing positive for monkeypox but has maintained that the virus is not sexually transmitted and is primarily spread through close contact.
- Less fever, fatigue -
Only 57 percent of the UK cases suffered fevers, compared to 85-100 percent of cases in outbreaks before this year.
Previous outbreaks also saw far more lesions on limbs, faces and necks.
However, in three quarters of the UK cases, lesions were only in one or two areas, mostly on or around genitals, the study said.
The UK patients also had mostly mild cases lasting fewer than three days, with just five being hospitalised.
The study's lead author Nicolo Girometti said that the UK's definition of monkeypox symptoms, which describes it as an acute illness with a fever, "should be reviewed to best adapt to the current findings".
"At least one in six of this cohort would have not met the current 'probable case' definition," said Girometti, of the Chelsea and Westminster Hospital NHS Foundation Trust.
Paul Hunter, an expert in infectious diseases at Britain's University of East Anglia not involved in the study, said he did not think the UK needs to change its monkeypox definition because it is currently "very broad".
Hugh Adler of the Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine told AFP it was unlikely that the monkeypox spreading globally represents a new form of the virus because other studies have shown "there have not been massive genetic changes".
Lesions on genitals suggests the virus is spreading in the UK via contact during sex, while previous African cases may have had lesions on their hands because they touched an infected animal or patient, he said.
He added that the study showed that monkeypox can initially resemble sexually transmitted diseases.
"Any new skin rash in a man who has sex with men should prompt consideration for monkeypox testing in the current climate, even if they have no other symptoms," he added.
F.Garcia--TFWP