CMSC
-0.0600


The United Nations on Tuesday warned the world to prepare for the effects of El Nino, saying the weather phenomenon which triggers higher global temperatures is set to persist throughout 2023.
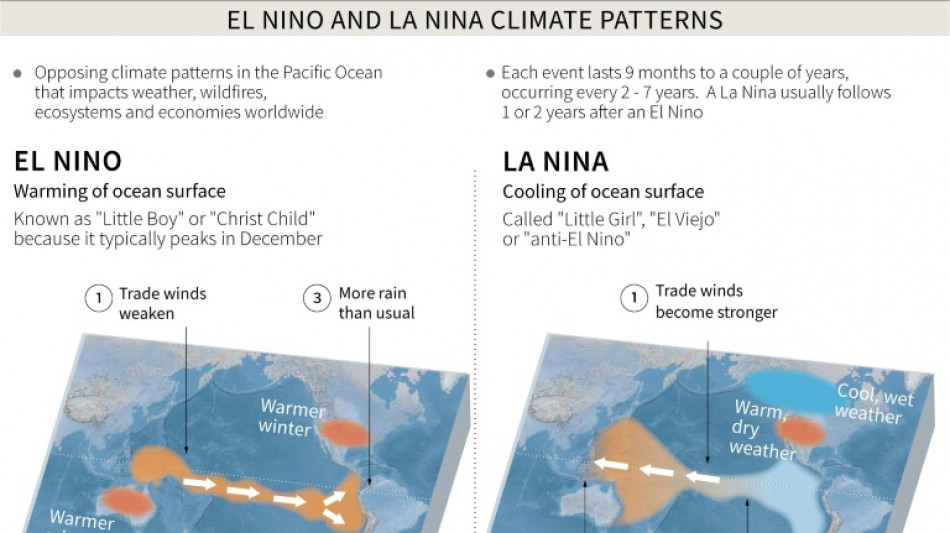
El Nino is a naturally occurring climate pattern typically associated with increased heat worldwide, as well as drought in some parts of the world and heavy rains elsewhere.
The phenomenon occurs on average every two to seven years, and episodes typically last nine to 12 months.
The UN's World Meteorological Organization declared El Nino was already under way and said there was a 90-percent chance that it would continue during the second half of 2023.
"The onset of El Nino will greatly increase the likelihood of breaking temperature records and triggering more extreme heat in many parts of the world and in the ocean," warned WMO secretary-general Petteri Taalas.
"The declaration of an El Nino by WMO is the signal to governments around the world to mobilise preparations to limit the impacts on our health, our ecosystems and our economies," said Taalas.
"Early warnings and anticipatory action of extreme weather events associated with this major climate phenomenon are vital to save lives and livelihoods."
The US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, which feeds into the WMO, announced on June 8 that El Nino had arrived.
"It is expected to be at least of moderate strength," the WMO said.
It noted that El Nino's warming effect on global temperatures is usually felt most strongly within a year of its onset -- in this case in 2024.
- Triple-dip La Nina over -
El Nino is the large-scale warming of surface temperatures in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean.
Conditions oscillate between El Nino and its generally cooling opposite La Nina, with neutral conditions in between.
El Nino events are typically associated with increased rainfall in parts of southern South America, the southern United States, the Horn of Africa and central Asia.
It can also cause severe droughts over Australia, Indonesia, parts of southern Asia, Central America and northern South America.
The WMO says the last El Nino was in 2015-2016.
From 2020 to early 2023, the world was affected by an unusually protracted La Nina, which dragged on for three consecutive years.
It was the first so-called triple-dip La Nina of the 21st century and only the third since 1950.
La Nina's cooling effect put a temporary brake on rising global temperatures, even though the past eight-year period was the warmest on record.
- Record predictions -
Wilfran Moufouma Okia, the WMO's head of regional climate prediction services, said that over the next six months, "there will be 10-percent chances for El Nino to weaken".
"So we can rule out the development of La Nina this year," he told reporters.
"The effect of El Nino is usually perceived with a delay in time," he added, with an eye on global temperatures increasing further.
In May, the WMO predicted a 98-percent likelihood that at least one of the next five years -- and the five-year period as a whole -- will be warmest on record.
Currently the hottest year on record is 2016, when there was an exceptionally strong El Nino, combined with human-induced heating from greenhouse gas emissions.
The UN's World Health Organization said it was helping countries prepare for the impact of El Nino, by pre-positioning stocks.
"In many of the countries that will be most affected by El Nino, there are already ongoing crises," warned Maria Neira, the WHO's environment, climate change and health director.
Extreme heat, wildfires and greater food insecurity leading to more acute malnutrition are also a cause for concern, she said.
P.Navarro--TFWP