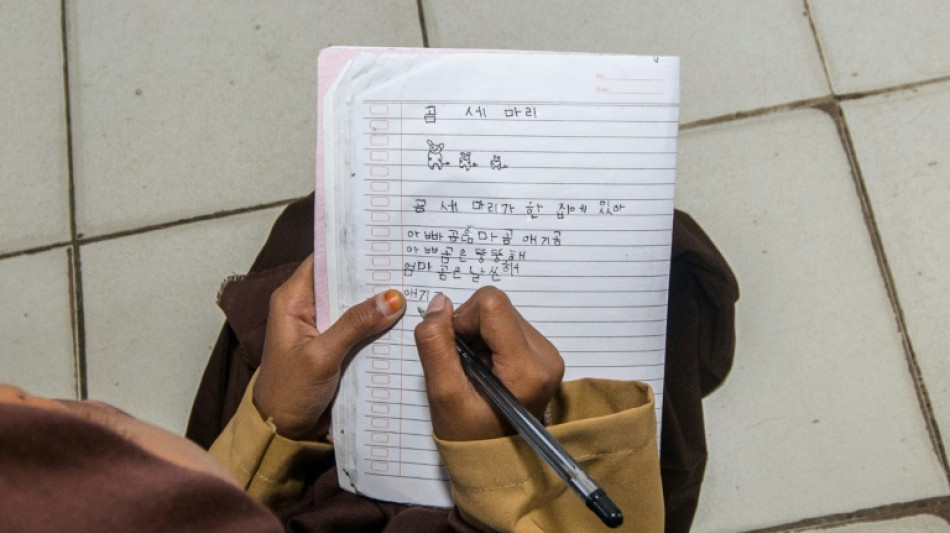
CMSD
0.0100

In an eastern Indonesian village, schoolchildren scrawl the distinctive circles and lines of Hangul script on a whiteboard, but the language they are learning is not Korean. It is their own Indigenous Cia-Cia tongue.
The language of the Cia-Cia ethnic group in southeast Sulawesi province's Baubau has no written form, and the syllable-based tongue does not readily translate to the Latin alphabet often used to transcribe Indonesia's national language.
But the Korean Hangul script, developed in the 15th century, shares a syllable-based system that has made it an unusual tool in the effort to preserve and transmit the language of the approximately 80,000 Cia-Cia people.
"In Latin words, for instance, there's no agreed way to pronounce the sounds 'pha' or 'ta'. But after I learned Korean, it turns out there are Korean characters for the sounds," 48-year-old teacher Abidin, who goes by one name, told AFP.
"They are not exactly the same, but they're similar."
Indonesia is a vast archipelago nation with myriad tribes and cultures that boasts more than 700 unique languages, making it one of the most linguistically diverse nations in the world.
The country's official language is Bahasa Indonesia, which owes its standard written form using Latin letters to Dutch colonial rule.
But the Cia-Cia's language had no surviving written form until 2009, when Hangul was introduced after a cultural exchange between Baubau city and Korean scholars.
The decision was the outcome of a concerted push by South Korean linguists, who visited to tout Hangul's sound-based system as the perfect fit.
After the visit, the city sent teachers and students to South Korea to learn Hangul with the goal of developing a standard way to write and teach their language.
- Preservation efforts -
In ancient times, leaders of the community committed the language to scraps of paper and wood using non-standard symbols that were never passed down and withered away.
But now Cia-Cia names dot the city's schools, streets and government institutions, rendered in Hangul.
The tongue is also taught to students from elementary to high school using Hangul symbols, though it remains largely a spoken rather than written language.
Abidin spent six months in South Korea training on Hangul, and is seen as a pioneer of transcribing Cia-Cia in the script. He has even penned a dictionary for the language using Hangul.
Hangul is viewed with great pride in South Korea, where it was once banned under Japanese rule, and word of the script's role in Indonesia has been hailed by some politicians and newspapers as proof of the writing system's global presence.
Its adoption by the Cia-Cia illustrated a fierce desire to preserve their language, said linguist Dalan Mehuli Perangin-angin at Indonesia's Sanata Dharma University.
"This shows that there is a longing from the people for their own script," he said.
Even the spoken form of Cia-Cia faces pressure from the dominance of Bahasa Indonesia and other regional languages, said Ilyas, a local elder, who goes by one name.
"Many words have been lost due to the influence of Indonesian and other regional languages. This has been happening for about 20 years," the 50-year-old said.
Fears about their language's future prompted elders to accept the use of Hangul, but some do have concerns.
- Language legacy -
Baubau is the only place in Indonesia to use Hangul, and while the South Korean push for the script is not backed by Seoul, its nationalist tint could blur the community's identity, said Periangin-angin.
"Language contains memories, history, morality, and wisdom of our ancestors. A language script is a legacy," he said.
He suggests the Cia-Cia could have adopted a script already used by another dialect in Sulawesi, which would have had closer linguistic links.
But for Sarianto, who was among the students who learned Hangul in South Korea, the script has "sparked the creation of new discourses dedicated to the preservation of the Cia-Cia language".
"Before the introduction of Hangul, many of Cia-Cia people used to feel a bit hesitant about using the local language in formal settings," he said.
"However, with the implementation of Hangul, people say our Cia-Cia language has become global."
F.Garcia--TFWP